|
Glaucoma is a group of diseases that can lead to damage to the eye's optic nerve. Open-angle glaucoma, the most common form of glaucoma, affects about 3 million Americans-half of whom don't know they have it. It has no symptoms at first. But over the years it can steal your sight. With early treatment, you can often protect your eyes against serious vision loss.
The optic nerve is a bundle of more than 1 million nerve fibers. It connects the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye, with the brain. A healthy optic nerve is necessary for good vision.

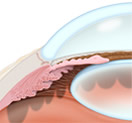
In many people, glaucoma is associated with high pressure inside the eye. In the front of the eye is a space called the anterior chamber. A clear fluid flows continuously in and out of this space and nourishes nearby tissues. The fluid leaves the anterior chamber at the angle where the cornea and iris meet. When the fluid reaches the angle, it flows through a spongy meshwork, like a drain, and leaves the eye.
Open-angle glaucoma gets its name because the angle that allows fluid to drain out of the anterior chamber is open. However, for unknown reasons, the fluid passes too slowly through the meshwork drain. As the fluid builds up, the pressure inside the eye rises. Unless the pressure inside the eye is controlled, it can damage the optic nerve and cause vision loss.
| |
 |
|
 |
|
| |
Normal Vision |
|
With Progressive Glaucoma |
|

Although anyone can get glaucoma, some people are at higher risk than others. Anyone with a family history of glaucoma should have check-ups by an ophthalmologist on a regular basis. Glaucoma is more common with advancing age. Certain medical conditions and medications can be associated with glaucoma.

Open-angle glaucoma most often has no symptoms. If left untreated, it can cause irreversible damage to your vision. The damage is often not noticeable to the individual in its early stages. Therefore early detection and treatment is essential to the long term health of your eyes.

 Most people think that they have glaucoma if the pressure in their eye is increased. This is not always true. High pressure puts you at risk for glaucoma. It may not mean that you have the disease. Whether or not you get glaucoma depends on the level of pressure that your optic nerve can tolerate without being damaged. This level is different for each person. Although normal pressure is usually between 12-21 mm Hg, a person might have glaucoma even if the pressure is in this range. That is why an eye examination is very important. Most people think that they have glaucoma if the pressure in their eye is increased. This is not always true. High pressure puts you at risk for glaucoma. It may not mean that you have the disease. Whether or not you get glaucoma depends on the level of pressure that your optic nerve can tolerate without being damaged. This level is different for each person. Although normal pressure is usually between 12-21 mm Hg, a person might have glaucoma even if the pressure is in this range. That is why an eye examination is very important.
To detect glaucoma, your eye care professional will do the following tests:
-
Visual acuity: This eye chart test measures how well you see at various distances.
-
Tonometry: This standard test determines the fluid pressure inside the eye. There are many types of tonometry. One type uses a purple light to measure pressure. Another type is the "air puff," test, which measures the resistance of the eye to a puff of air.
-
Pupil dilation: This examination provides your eye care professional with a better view of the optic nerve to check for signs of damage. To do this, your eye care professional places drops into the eye to dilate (widen) the pupil. After the examination, your close-up vision may remain blurred for several hours.
-
Visual Field: This test measures your side (peripheral) vision. It helps your eye care professional find out if you have lost side vision, a sign of glaucoma.

Yes. This makes early diagnosis and treatment important to protect your sight. Most doctors use medications for newly diagnosed glaucoma; however recent research suggests that laser treatment can be a safe and effective alternative.

-
Medicine: Medicines are the most common early treatment for glaucoma usually in the form of eye drops. Some cause the eye to make less fluid and some lower the pressure by helping fluid drain from the eye. No single medicine works best in all individuals. Your ophthalmologist may try different medicines to see which one works best in your case. Because glaucoma often has no symptom, people may be tempted to stop or may forget to take their medicine. It is very important to take your medicine daily and consistently to prevent the progression of glaucoma.
-
Laser treatment: (also called laser trabeculoplasty): Laser treatment helps fluid drain out of the eye. Although your eye care professional may suggest laser treatment at any time, it is often done after trying treatment with medicines first. In some cases, you will need to keep taking glaucoma medicine even after laser treatment.
-
Conventional surgery: The purpose of surgery is to make a new channel for the fluid to leave the eye. Glaucoma surgery is most often done after medicine and laser treatment have failed to control your eye pressure. This surgery is performed in an operating room at an outpatient surgery center which is specialized for eye surgery.

Although open-angle glaucoma is the most common form, some people have other forms of the disease. A variant of open-angle glaucoma is low tension or normal tension glaucoma. In low tension glaucoma, the optic nerve can be damaged even though the pressure inside the eye is normal. The treatment is similar to open-angle glaucoma associated with high pressure inside the eye.
| |
|
| |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| |
Open-Angle |
|
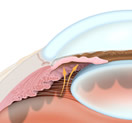
Closed-Angle |
|
Narrow Angle |
|
In closed-angle glaucoma, the fluid at the front of the eye cannot reach the angle and leave the eye because the angle gets blocked by part of the iris. People with this type of glaucoma have a sudden increase in pressure. Symptoms include severe pain and nausea as well as redness of the eye and blurred vision. This is a medical emergency. The patient needs immediate treatment to improve the flow of fluid. Usually, prompt laser treatment can clear the blockage and protect sight.
Secondary glaucomas can develop as a complication of other medical conditions. They are sometimes associated with eye surgery or advanced cataracts, eye injuries, uveitis (eye inflammation), and retinal vascular problems. Pigmentary glaucoma occurs when pigment from the iris flakes off and blocks the meshwork, slowing fluid drainage. Treatment is with medicines, laser procedures, or sometimes conventional surgery.

If you are being treated for glaucoma, be sure to take your glaucoma medicine every day and see your eye care professional regularly. You can also help protect the vision of family members by encouraging them to have an eye examination.
Feel free to contact us for any further information about the diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma.
|